|
Solution Components
|
A Sub-Function: Measure pedal movement |
A.1- Potentiometer
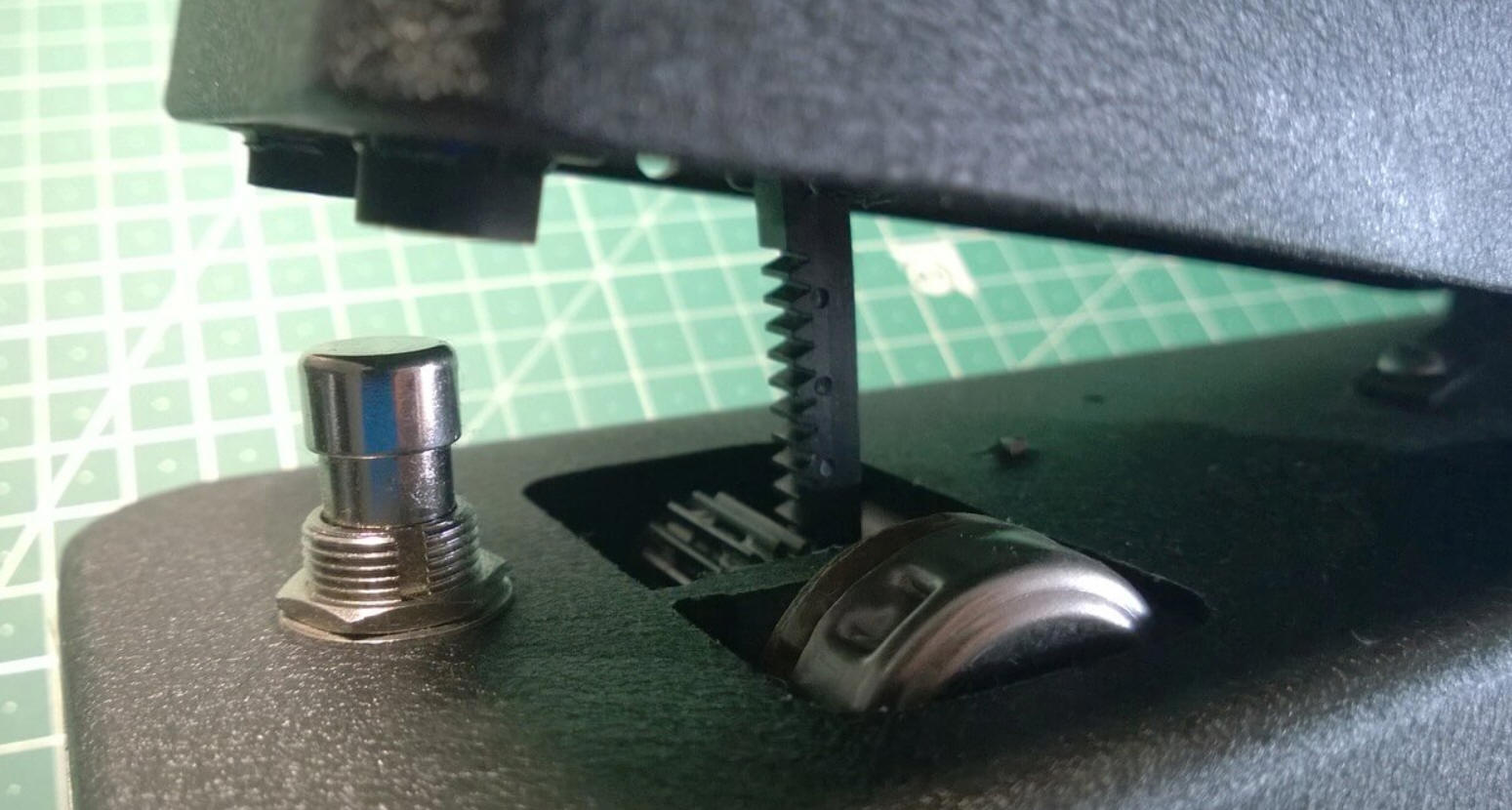 |
| Fig: Potentiometer setting via rack
in a wah pedal (source) |
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Cheap |
|
| Ready-made
variants available in pedal form |
|
| A Subfunction: Measurement
of pedal movement |
A.2 - Inductive displacement sensor
 |
| Fig. Inductive displacement sensor(Source) |
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| |
Expensive |
| |
Implement connection to pedal |
| A Subfunction: measure
pedal movement |
A.3 -Incremental encoder
|
Advantages: |
DIsadvantages: |
| Direction of
rotation could be used as an input variable by the user of
the pedal |
More expensive than potentiometers
|
| B Subfunction: Process
input data and derive actuator signal |
B.1 Microcontroller
 |
| Fig: Mikrocontroller ESP32
LOLIN
(Source) |
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| Cheap |
|
|
More energy efficient |
|
| flexible
application possibilities |
|
|
B Subfunction: Process
input data and derive actuator signal |
B.1 Programmable logic controller
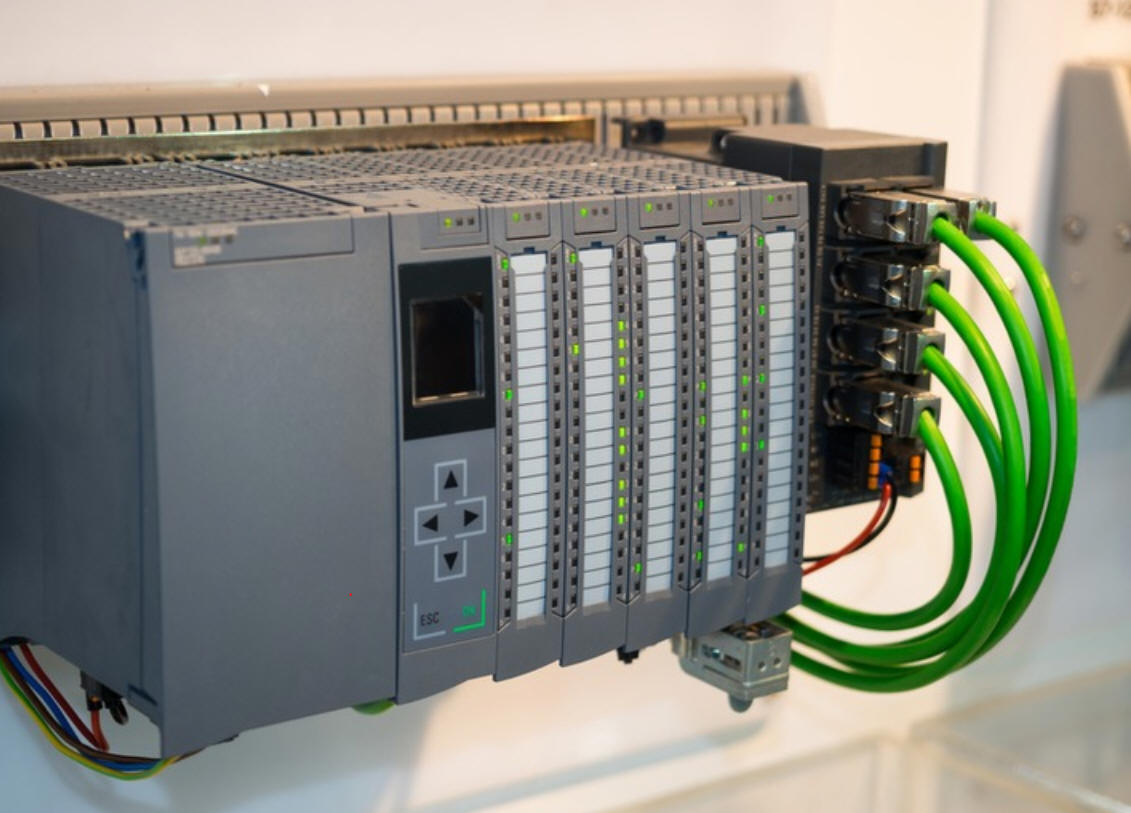 |
| Fig: Programmable logic controller |
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| |
Program processing cyclically with
lower frequency |
| |
Expensive |
| C Partial function: reduce
free cord length |
C.1 Winding the line on a winch by means of a motor
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| Conversion of
translational movement into rotational movement |
|
| Clean line
storage without knotting |
|
|
D
Subfunction: increase free cord length |
D.1 Mechanical freewheel
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| low mass |
|
|
lowest possible moment of inertia during climb, as other
parts remain unmoved |
|
| D Subfunction: reduce free
cord length |
D.2 Turning of the drive unit (winch wheel to rotor of the
motor)
 |
| Fig.: Stepper motor with coupling
on a shaft
(Source) |
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| few components
needed |
Motor will apply counter-torque |
| Revolutions in
climb could be determined --> rope length could be
determined in the system |
|
| E Subfunction: Torque
transmission from drive to winch |
E.1 - mounting the winch on a shaft; The shaft is driven by a
bellows coupling
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| Rigid
connection, no loss of kinetic energy through damping in
elastic components |
high accuracy requirements for the
assembly of the shafts (axial, radial & angular dimension) |
| E Subfunction: Torque
transmission from the drive to the winch |
E.2 - mounting the winch on a shaft; The shaft is driven by a
double loop clutch
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
|
anti-vibration |
Speed limitation (usually up to
3000 rpm) |
|
Inaccuracies when aligning the shafts do not endanger
concentricity |
|
|
| E Subfunction: Torque
transmission from the drive to the winch |
E.3 - Motor shaft to shaft connection with winch via belts
 |
| Fig: Belt connection and with drive
(Source) |
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| |
higher number of components:
transmission pinion, more roller bearings |
|
|
F
Subfunction: Motor variant |
F.1 - DC motor
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| higher speeds
can be achieved |
|
| faster
response time compared to a stepper motor |
|
| F Subfunction: Motor
variant |
F.2 - Stepper motor
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| no rotary
encoder necessary |
speeds limited |
| easily
controllable via microcontroller |
|
| F Subfunction: Motor
variant |
F.3 - Servomotor
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| Accurate
positioning |
usually no continuous rotations |
| accurate
position feedback |
speeds limited |
| G Subfunction: line
guide for flight near the ground (takeoff and landing) |
G.1 - Elevation of the drone by landing gear
 |
| Fig: Elevation of the drone by
landing gear(Source) |
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| Increasing the
distance between the rotors and the line lying on the ground
--> less likely to get caught |
additional weight for the drones |
| low mass |
possibly slight negative impact on
flight duration |
| G
Subfunction: line guide for flight near the ground (takeoff
and landing) |
G.2 - Loading on elevated platform
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| Erhöhung
Abstand zwischen Rotoren und auf Boden aufliegender Schnur
--> "Verfangen" unwahrscheinlicher |
Mobilität des Aufbaus deutlich
reduziert |
| G
Subfunction: line guide for flight near the ground (takeoff
and landing) |
G.3 -Line guide through eyelet near the bottom
 |
| Fig: Eyelet(ring) that can be
brought close to the ground during takeoff and landing
(Source) |
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
|
Easy to use |
Eyelet must be
folded up during operation to avoid increased friction |
| Ensuring that
line is kept away from rotors at a favorable angle |
|
| H Sub-function:
energy supply of the system |
H.1 - a battery for the supply of the data processing unit and a
battery for the motor
  |
| Fig: Separate batteries for
microcontroller and motor |
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| simple
interconnection |
costly |
| Batteries can
be replaced individually if there is a high energy
requirement |
|
| H Sub-function:
energy supply of the system |
H.2- One battery for the entire system with use of optocouplers
| Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| only one
battery required |
more
complex wiring |
| inexpensive |
|
| I Sub-function:
energy supply of the drone(on the drone) |
I.1 - Directly replace the original drone battery with the power
supply via a
cable
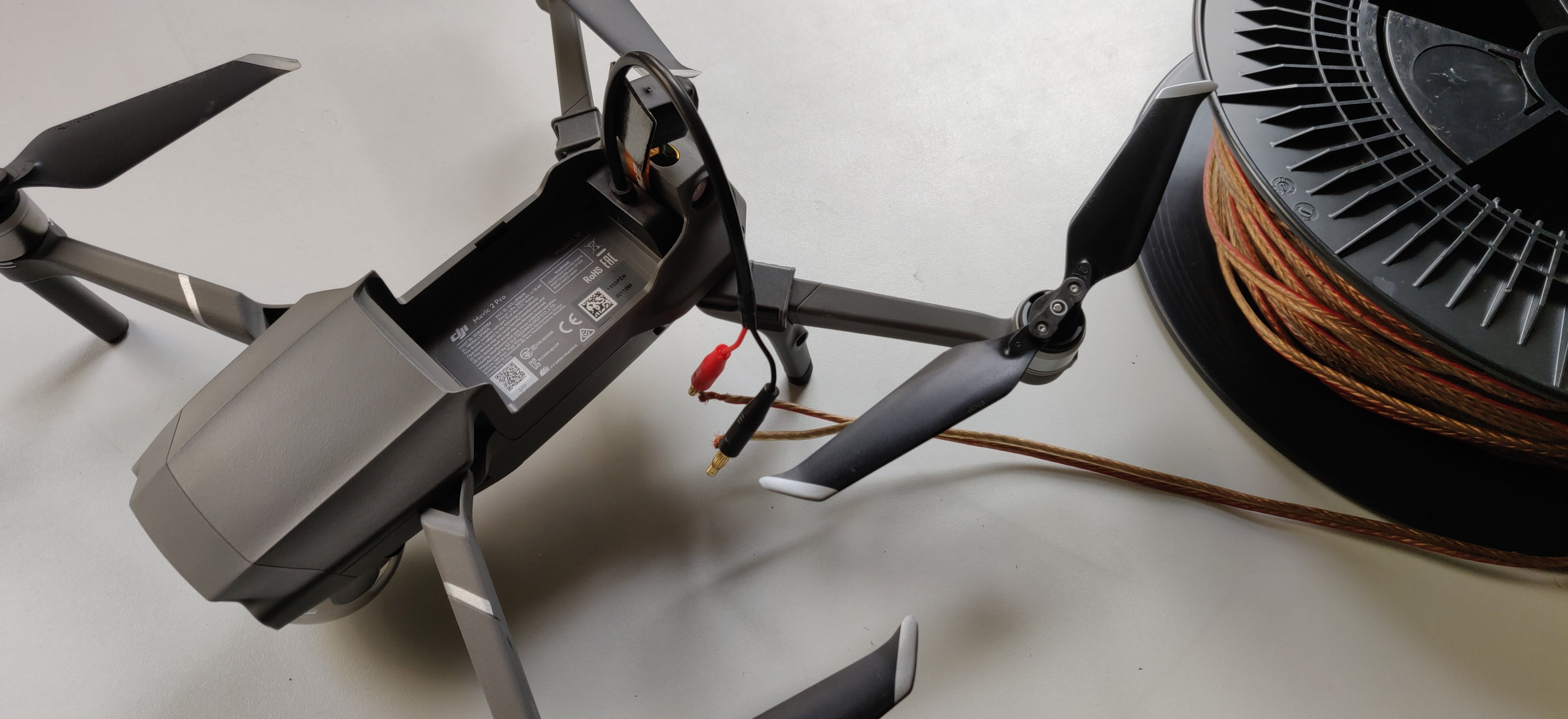 |
| Fig: Power supply with a
cable(without battery) |
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| Allow light
weight system |
DJI Mavic 2 has an intelligent
battery which allow to start the drone. So we would need to
install and program a microcontroller to turn the drone on. |
| No flight time
limitation |
Complex system |
| I Sub-function:
energy supply of the drone(on the drone) |
I.2- STARTRC For DJI Mavic 2 Battery Extended Adapter to extract
an input power with Drone battery
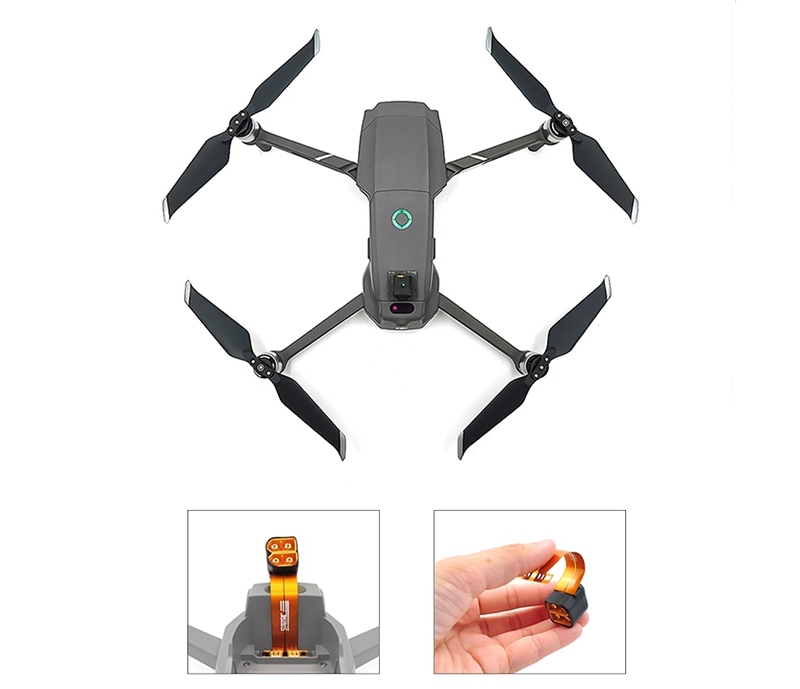 |
| Fig: Power supply via STARTRC
adapter (with battery) |
| Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| Don´t need to
remove the original battery |
More weight |
| No flight time limitation |
|
|
J Sub-function:
Energy supply of the drone(on the ground) |
J.1 - Sliding electrical contact
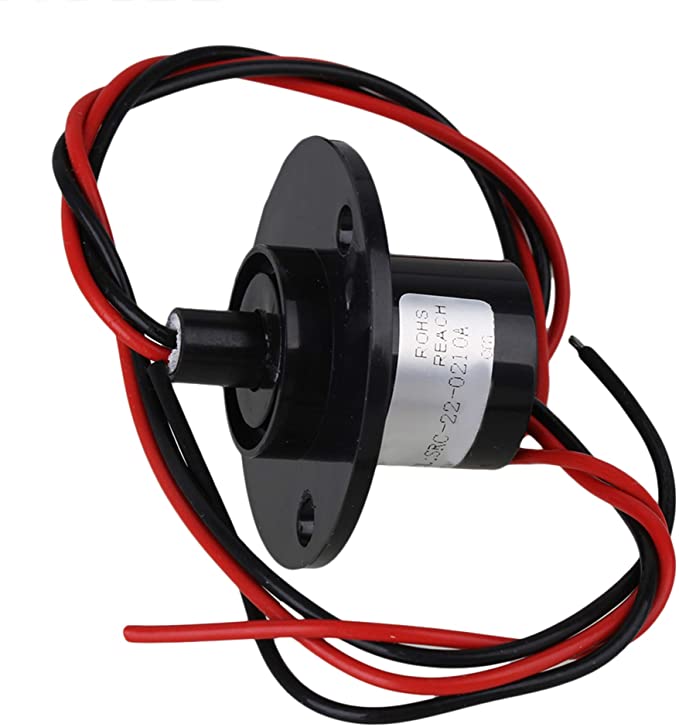 |
| Fig: Sliding Contact BQLZR |
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
|
Transfer of energy |
wear of
sliding contacts |
| Rotating
connection |
|
|
J Sub-function:
Energy supply of the drone(on the ground) |
J.2- Inductive power supply
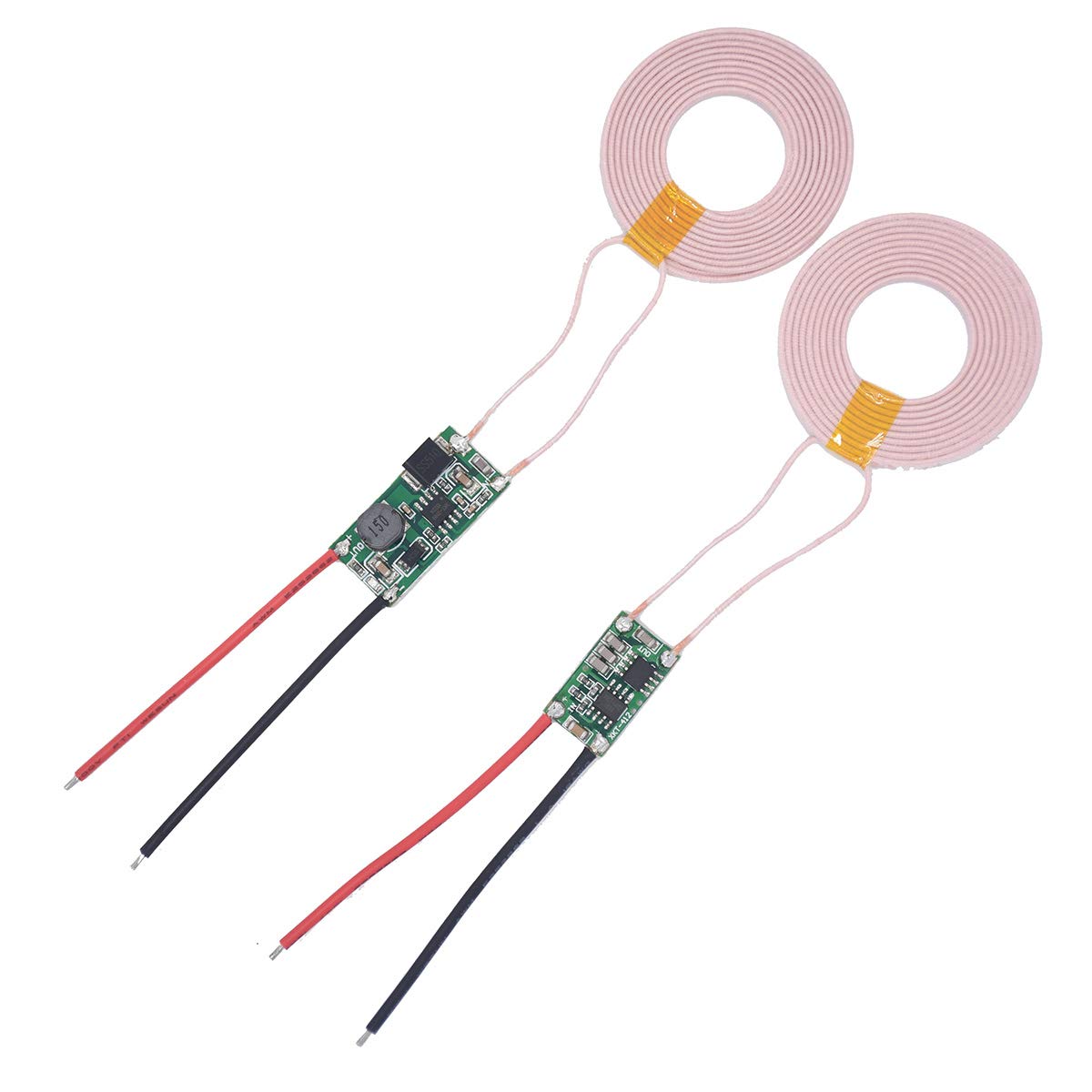 |
| Fig: Wireless power supplier |
| Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
| Non-contact
transmitter reciever |
Large surface
for energy |
| |
loss of energy |
|

